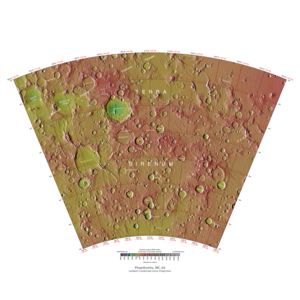
Phaethontis quadrangle
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1]
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
283621 characters 21 sections 107 paragraphs 96 images 330 internal links 116 external links |
2. Associated features of gullies 6. Magnetic stripes and plate tectonics |
hiwish 0.388 gullies 0.354 hirise 0.339 phaethontis 0.261 program 0.216 mantle 0.149 ice 0.144 crater 0.121 view 0.119 stripes 0.118 gully 0.114 image 0.106 sirenum 0.106 concentric 0.103 glaciers 0.103 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] |
| 2017 |
272712 characters 20 sections 99 paragraphs 89 images 327 internal links 112 external links |
5. Magnetic stripes and plate tectonics |
hiwish 0.394 gullies 0.338 hirise 0.329 phaethontis 0.280 program 0.220 mantle 0.153 ice 0.134 stripes 0.127 crater 0.115 sirenum 0.114 magnetic 0.106 image 0.106 gully 0.100 craters 0.100 view 0.100 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] |
| 2016 |
251474 characters 17 sections 119 paragraphs 115 images 307 internal links 76 external links |
5. Magnetic Stripes and Plate Tectonics 7. Fossae in Phaethontis quadrangle 8. Strange Surfaces in Phaethontis quadrangle |
gullies 0.346 hiwish 0.337 hirise 0.297 phaethontis 0.260 crater 0.207 program 0.189 ctx 0.182 image 0.157 reconnaissance 0.145 mantle 0.122 enlargement 0.118 camera 0.114 stripes 0.113 copernicus 0.105 orbiter 0.103 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] The Phaethontis quadrangle lies between 30° and 65 ° south latitude and 120° and 180 ° west longitude on Mars . This latitude range is where numerous gullies have been discovered. An old feature in this area, called Terra Sirenum lies in this quadrangle; Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter discovered iron/magnesium smectites there. [2] Part of this quadrangle contains what is called the Electris deposits , a deposit that is 100–200 meters thick. It is light-toned and appears to be weak because of few boulders. [3] Among a group of large craters is Mariner Crater , first observed by the Mariner IV spacecraft in the summer of 1965. It was named after that spacecraft. [4] A low area in Terra Sirenum is believed to have once held a lake that eventually drained through Ma'adim Vallis . [5] [6] Russia's Mars 3 probe landed in the Phaethontis quadrangle at 44.9° S and 160.1° W in December 1971. It landed at a speed of 75 km per hour, but survived to radio back 20 seconds of signal, then it went dead. Its message just appeared as a blank screen. [7] |
| 2015 |
224350 characters 13 sections 99 paragraphs 97 images 277 internal links 75 external links |
4. Magnetic Stripes and Plate Tectonics 6. Fossae in Phaethontis quadrangle 7. Strange Surfaces in Phaethontis quadrangle |
gullies 0.386 phaethontis 0.290 hiwish 0.253 hirise 0.251 crater 0.213 ctx 0.203 image 0.170 reconnaissance 0.161 program 0.146 mantle 0.135 enlargement 0.131 camera 0.127 stripes 0.126 copernicus 0.117 orbiter 0.114 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] The Phaethontis quadrangle lies between 30° and 65 ° south latitude and 120° and 180 ° west longitude on Mars . This latitude range is where numerous gullies have been discovered. An old feature in this area, called Terra Sirenum lies in this quadrangle; Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter discovered iron/magnesium smectites there. [2] Part of this quadrangle contains what is called the Electris deposits , a deposit that is 100–200 meters thick. It is light-toned and appears to be weak because of few boulders. [3] Among a group of large craters is Mariner Crater , first observed by the Mariner IV spacecraft in the summer of 1965. It was named after that spacecraft. [4] A low area in Terra Sirenum is believed to have once held a lake that eventually drained through Ma'adim Vallis . [5] [6] Russia's Mars 3 probe landed in the Phaethontis quadrangle at 44.9° S and 160.1° W in December 1971. It landed at a speed of 75 km per hour, but survived to radio back 20 seconds of signal, then it went dead. Its message just appeared as a blank screen. [7] |
| 2014 |
172357 characters 9 sections 48 paragraphs 47 images 260 internal links 71 external links |
2. Magnetic Stripes and Plate Tectonics 4. Fossae in Phaethontis quadrangle |
gullies 0.479 hirise 0.253 phaethontis 0.234 stripes 0.212 hiwish 0.206 sirenum 0.170 magnetic 0.165 mantle 0.161 electris 0.133 program 0.129 aquifer 0.128 aquifers 0.127 ice 0.112 image 0.109 flow 0.105 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] The Phaethontis quadrangle lies between 30° and 65 ° south latitude and 120° and 180 ° west longitude on Mars . This latitude range is where numerous gullies have been discovered. An old feature in this area, called Terra Sirenum lies in this quadrangle; Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter discovered iron/magnesium smectites there. [2] Part of this quadrangle contains what is called the Electris deposits , a deposit that is 100–200 meters thick. It is light-toned and appears to be weak because of few boulders. [3] Among a group of large craters is Mariner Crater , first observed by the Mariner IV spacecraft in the summer of 1965. It was named after that spacecraft. [4] A low area in Terra Sirenum is believed to have once held a lake that eventually drained through Ma'adim Vallis . [5] [6] Russia's Mars 3 probe landed in the Phaethontis quadrangle at 44.9° S and 160.1° W in December 1971. It landed at a speed of 75 km per hour, but survived to radio back 20 seconds of signal, then it went dead. Its message just appeared as a blank screen. [7] |
| 2013 |
170667 characters 9 sections 48 paragraphs 46 images 261 internal links 71 external links |
2. Magnetic Stripes and Plate Tectonics 4. Fossae in Phaethontis quadrangle |
gullies 0.479 hirise 0.253 phaethontis 0.234 stripes 0.212 hiwish 0.206 sirenum 0.170 magnetic 0.165 mantle 0.161 electris 0.133 program 0.129 aquifer 0.128 aquifers 0.127 ice 0.112 image 0.109 flow 0.105 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] The Phaethontis quadrangle lies between 30° and 65 ° south latitude and 120° and 180 ° west longitude on Mars . This latitude range is where numerous gullies have been discovered. An old feature in this area, called Terra Sirenum lies in this quadrangle; Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter discovered iron/magnesium smectites there. [2] Part of this quadrangle contains what is called the Electris deposits , a deposit that is 100–200 meters thick. It is light-toned and appears to be weak because of few boulders. [3] Among a group of large craters is Mariner Crater , first observed by the Mariner IV spacecraft in the summer of 1965. It was named after that spacecraft. [4] A low area in Terra Sirenum is believed to have once held a lake that eventually drained through Ma'adim Vallis . [5] [6] Russia's Mars 3 probe landed in the Phaethontis quadrangle at 44.9° S and 160.1° W in December 1971. It landed at a speed of 75 km per hour, but survived to radio back 20 seconds of signal, then it went dead. Its message just appeared as a blank screen. [7] |
| 2012 |
168510 characters 9 sections 49 paragraphs 44 images 261 internal links 70 external links |
2. Magnetic Stripes and Plate Tectonics 4. Fossae in Phaethontis quadrangle |
gullies 0.479 hirise 0.253 phaethontis 0.234 stripes 0.212 hiwish 0.206 sirenum 0.170 magnetic 0.165 mantle 0.161 electris 0.133 program 0.129 aquifer 0.128 aquifers 0.127 ice 0.112 image 0.109 flow 0.105 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] |
| 2011 |
113660 characters 8 sections 42 paragraphs 33 images 120 internal links 65 external links |
2. Magnetic Stripes and Plate Tectonics |
gullies 0.508 phaethontis 0.248 stripes 0.224 hirise 0.215 magnetic 0.175 sirenum 0.157 mantle 0.156 electris 0.141 hiwish 0.137 aquifer 0.136 aquifers 0.135 ice 0.119 flow 0.111 image 0.108 water 0.104 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] |
| 2010 |
65028 characters 8 sections 35 paragraphs 26 images 109 internal links 12 external links |
2. Magnetic Stripes and Plate Tectonics |
gullies 0.474 phaethontis 0.271 stripes 0.245 magnetic 0.191 mantle 0.171 hirise 0.166 electris 0.155 aquifer 0.149 aquifers 0.148 ice 0.130 flow 0.121 water 0.114 magnetism 0.112 image 0.111 slopes 0.109 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program . The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). [1] |
| 2009 |
38603 characters 6 sections 26 paragraphs 17 images 96 internal links 4 external links |
stripes 0.358 gullies 0.310 phaethontis 0.296 magnetic 0.214 mantle 0.204 click 0.159 aquifer 0.145 hirise 0.143 magnetized 0.132 flow 0.124 ice 0.118 water 0.116 chloride 0.109 mariner 0.109 aquifers 0.108 |
The Phaethontis quadrangle lies between 30° and 65 ° south latitude and 120° and 180 ° west longitude on Mars . This latitude range is where numerous gullies have been discovered. Around a group of large craters is Mariner Crater , first observed by the Mariner IV spacecraft in the summer of 1965. It was named after that spacecraft. [1] Russia's Mars 3 probe landed in the Phaethontis quadrangle at 44.9° S and 160.1° W in December 1971. It landed at a speed of 75km per hour, but survived to radio back 20 seconds of signal, then it went dead. Its message just appeared as a blank screen. [2] |